Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayYou may have found yourself in a situation where you set up a brand new unit and rack it just to find out that you misconfigured it in some way and the craft cable just isn't quite long enough. You know the IP address of the unit, so you think, is there some way I can quickly get back into this unit's terminal?
At DPS, we've given careful thought into facilitating a multitude of ways to communicate with our devices. So much, in fact, that our T/Mon supports over 25 modern and legacy protocols to keep you connected to even your remotest sites.
In this scenario, you may also consider navigating to your device's web interface to configure your device, but in this article, I want to cover Telnet. We have supported Telnet in our devices for a long time now, but a common question we get is if our devices support Telnet, and, if so, how do I get started with something like that? So, let's take a look at Telnet and how to communicate with a NetGuardian using it.
Telnet, short for "Teletype Network", is an application layer protocol designed for bidirectional interactive text-based communication between a client and a server. While Telnet communicates over TCP, the connection is interspersed with additional control information.
Telnet is similar to SSH in that it facilitates a command line interface on a remote host. However, due to risk of eavesdropping over public networks, SSH tends to be the preferred method of this type of communication.
Practically, you will be using Telnet to connect to a nearby device that is already on the same network, but where a craft cable may be just too short. Or you will use Telnet when your network is large enough that long distance won't put you on a public network or the general Internet.
When it comes to choosing a program, a couple come to mind. There really is no right or wrong application, and the most popular triad of operating systems—Windows, MacOS, and Linux—support Telnet out of the box.
A few applications we recommend are TeraTerm, PuTTY, and Windows Command Prompt (or CMD.exe). All you really need is a Terminal emulator and a Telnet client. For example, one might prefer to use PuTTY because it has a build-in client that does not need administrative permissions to use, unlike the built-in Windows Telnet client, which requires admin privileges to enable or disable.
For this demonstration, I will be using Windows 10 and PuTTY to connect to my NetGuardian. However, I will also cover how to enable Telnet on Windows in case PuTTY is not installed or is not preferred.
Before we begin this step, it is important that you first make sure that the user account on your PC has elevated permissions. It can be a real sense of grief to go through the process of enabling Telnet only to find out that you lack the privileges to do so.
The process of enabling Telnet is similar on both Windows 7 and Windows 10. On either platform, open the start menu. On Windows 7, you will click on "Control Panel". On Windows 10, you will simply type "Control Panel" and then click on the app that is the best match.
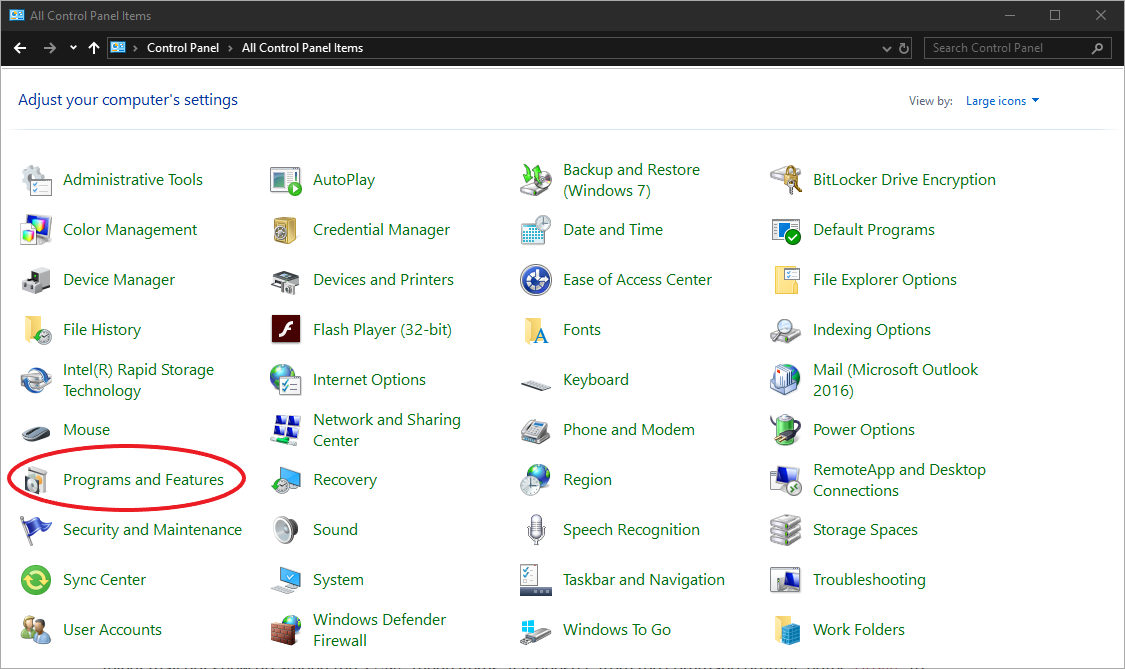
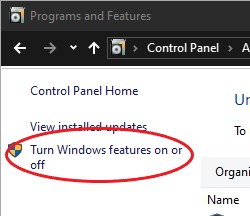
In the Control Panel, click "Programs and Features", then click on "Turn Windows Features On or Off" in the upper left-hand corner. From the Windows Features list that appears, locate and check "Telnet Client".
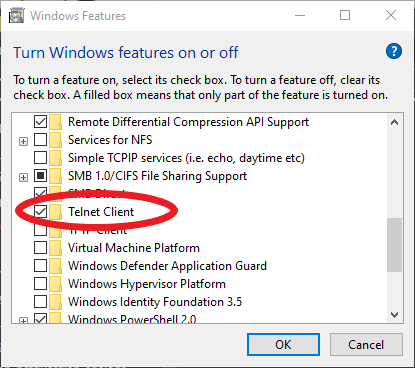
From here, go ahead and click OK and wait for the new service to provision. Once it's finished, go ahead and close out of all Control Panel windows.
Now that Telnet is configured, let's get into our device. I will assume a few preconditions before moving forward:
With PuTTY open, select the Telnet connection type, then type in the IP address, and also change the port from 23 to 2002. Conventionally, Telnet uses port 23 by default, but our devices use port 2002 by default for Telnet.
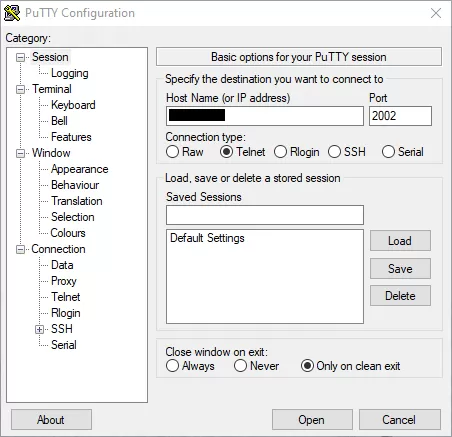
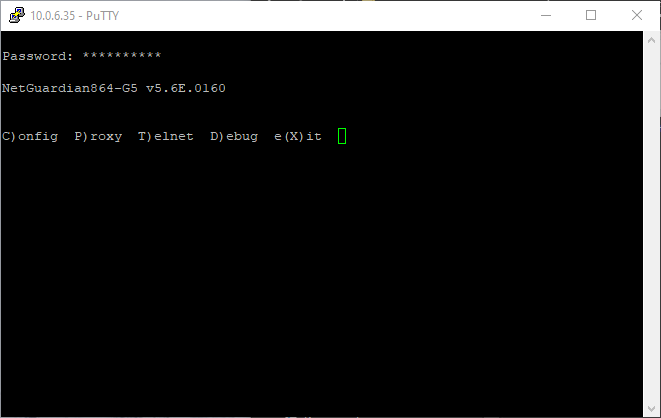
And that's it! We've successfuly connected to our device using Telnet. If you're not using PuTTY to connect to the RTU and instead are using the Telnet command, the process is relatively easy. Enter the command below:
telnet <IP_ADDRESS> 2002 In the same Telnet window that we have open, we can also Telnet into another device. This is practical if you have a direct line to one NetGuardian, but other devices behind it are either on a different subnet, or belong on their own network entirely.
From the current window, type "T" for Telnet, then enter just the IP address of another device on the same subnet as the current NetGuardian, and finally enter the port number when prompted. A connection will be established to the RTU, verifying both connectivity over port 2002 and also connection over IP.
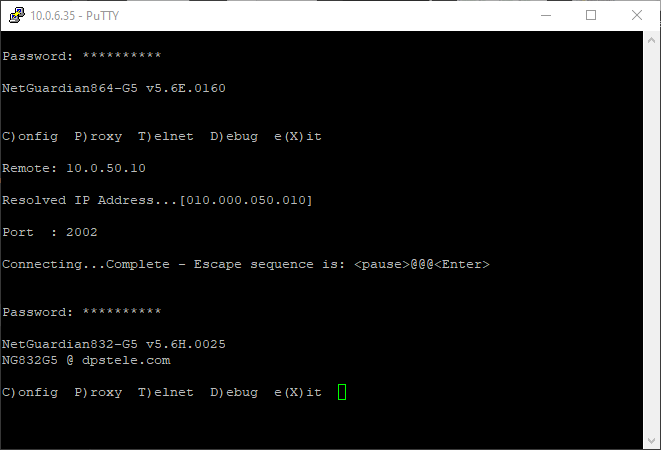
You can see from the picture above that we have first logged in to one RTU, then logged into another RTU through that connection. While this is not ideally what you will see out in the field, this is a great way of verifying port availability, as well as being able to remotely configure a device that may be on a different network, effectively using the host NetGuardian as a static route.
Telnet is a great tool that allows us to use the same Craft interface from a distance. It is useful when the Craft cable may not be long enough, or your office is a ways away. Either way, we hope this article has equipped you with an understanding of how Telnet works and how our devices utilize it.
If you have any further questions on setup or are encountering other issues, give us a call and our expert tech support would be more than happy to assist in any way we can.

Julian Coleman
Julian Coleman is a Software Engineer at DPS Telecom. He is responsible for maintaining internal tool systems and improving website UX.