Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat Today
Managed switches can play an essential role in your overall network health. But, do you know enough about them to make the right decisions?
As a monitoring and control solutions manufacturer, we are specialists when it comes to managing network health. Providing perfect-fit systems has been our goal for the last 30 years, and we our priority is customer satisfaction - that's why we want you to know how you to make an informed decision before anything else.
Let's go over some practical information about managed switches, how you can choose an effective switch for your network system, and alternative tools that also can help you manage your network.
Network switches are boxes that allow the connection of different devices together on a Local Area Network (LAN). There are two different kinds of switches: managed and unmanaged.
The main difference between a managed switch and an unmanaged one is the capacity of configuring the switch and prioritizing LAN traffic in order to make sure that the most important data goes through.
An unmanaged switch permits Ethernet devices to talk to each other, and that's pretty much all that they do. For example, consider the connection of a network printer to a PC - although you'll probably see the plug 'n' play feature, you won't be able to make any changes to the configuration in order to make it work how you want since it's locked.
On the other hand, a smart managed switch uses protocols, generally the SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), to monitor devices present in the network and get information like the status of connections, the statistics of traffic throughput, network errors, and port status.

This means that SNMP queries can assess the health of the network or the status of a determined device. The SNMP protocol is the responsible for displaying the information in an easy-to-understand format, so network administrators can monitor the network and quickly detect and respond to any issues without having to physically go to a remote site.
Setting these smart switches up may take a little longer in comparison to unmanaged switches because the second ones generally have the plug and play capability.
Another big difference between managed and unmanaged switches, of course, is their prices.
Managed switches usually are much more expensive than the unmanaged ones. But that's because they do offer more features, which often include:
Ability to implement Quality of service (QoS)
Support for virtual LANs (VLANs)
Port mirroring, and
Support for Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
These features are responsible for helping to control the traffic traveling over the managed switch. Let's go over each of them.
Quality of service enables you to set priorities in your network traffic by giving top priority to the most important data.
This makes sure that your network is running consistently and supports time-sensitive information, like real-time voice. Imagine just how frustrating it is to miss half of what a caller is trying to say because voice packets got delayed - now you can't understand your conversation.
Imagine you want to segment traffic between your finance and marketing groups in order to make the significant finance information flow without obstruction to the finance department and not get jammed by the marketing traffic.
That's where the VLAN will come into play. It allows a switch to logically gather groups together to segregate traffic between these groups even when the traffic is running over the same physical switch.
VLAN improves the network efficiency and - more often than not - provides an additional level of security.
The port mirroring feature works with a network analyzer to enforce policies, detect intrusions, to monitor and predict traffic patterns, correlate events, and so on.
It works by copying the switch network traffic and forwarding it to a single port on the same switch for analysis by a network analyzer.
Another important feature of a managed switch is redundancy. This feature protects a network in case a connection is lost or a cable fails, it is done by an alternate data path or traffic.
The network redundancy in managed switches is due to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). The STP only allows one active path at a time between two network devices, which avoids loops, establishes the redundant links as a backup to keep integrated systems available, and prevents expensive downtime.
First of all, you need to evaluate the needs of your network. The best type of switch for you will depend on your scenario and requirements.
If your network necessities have grown to a point where it's necessary to monitor and control the traffic behavior over your LAN, then it's strongly recommended considering a managed switch. They are designed to handle intense workloads, high amounts of traffic and deployments where custom configurations are a necessity.
On the other hand, if all you need is to add additional Ethernet ports to your network - with the peace to connect everything up and get going - unmanaged switches would be the best option for you. They are best suited for home and small offices use.
Not all managed switches are created equal though, so if you decided that this is the best option for your scenario, it's vital that you know the main points that an efficient switch must have.
Your managed switch is one of the most important pieces of equipment in your business infrastructure.
If you don't monitor your switches carefully, your customers can be frustrated by extended outages. Effective network alarm monitoring minimizes and can even prevent these reputation-damaging outages. It gives you the visibility you need to quickly resolve your switch problems before they grow into bigger threats.
Having a managed switch with monitoring functionality embedded has its value, and can be a good solution for achieving network visibility, as long as it comes from a reliable manufacturer.
However, a switch-only manufacturer isn't a monitoring specialist and can't provide you with the important functions that a monitoring solutions developer can. So, if your switch manufacturer is not specialized in monitoring solutions as well (), your managed switch might not be something you can trust with your critical infrastructure. For these cases, it's better to invest in an advanced switch monitoring system.
Here are seven key elements of an effective switch monitoring system:
Multiprotocol support
An efficient switch monitoring system will collect alarms from all of your equipment, regardless of manufacturer or protocol. This means that your system will bring together, under only one screen, devices that otherwise would be incompatible.
Email and cell phone notifications
A high-quality switch monitoring system will also automatically send detailed notifications to technicians by email and text message. So, you and your techs would know on a timely-manner when a problem arises and can take action before this problem escalates. Without meaningful alarms, you'll never know how to properly respond to an emergency on your network.

Control relays
Find a switch monitoring system that will allow for remote operation of site devices, such as generators and cooling systems. This is an excellent way to eliminate unnecessary site visits and expensive truck rolls.
Intelligent alarm organization
A large, complex network can create a cascade of alarms. Some are unimportant, but others are critical. Look for a monitoring system that can automatically sort and prioritize this flood of information for you, displaying alarms filtered by site, severity, and other criteria as you see fit. In a case of emergency, you'll be able to see quickly what your highest priority alarms are.
History and trend analysis
Another feature that any effective monitoring system should have is a complete alarm history that is exportable for trend analysis. This can be used to identify trouble areas and eliminate recurring problems.
Nuisance alarm filtering
You should be able to filter out status alerts, oscillating conditions, and unimportant alarms. This is important as your staff may stop taking alarms seriously if they are bombarded with repetitive, unimportant alerts.
Live analog monitoring
The analog input feature - with live monitoring of actual analog value - is an essential capability of a high-quality switch monitoring system. Analog monitoring allows you to accurately measure and report important values, such as temperature, humidity, and fuel levels. These factors affect the condition of your valuable equipment at your remote sites.
The second best practice when choosing a managed switch is finding one with Power over Ethernet feature. Power over Ethernet, or simply PoE, greatly simplifies wiring, as it provides both data and power connections in one cable so equipment doesn't require a separate cable for each need.
For equipment doesn't already have a power or data connection, PoE can be attractive when the power demand is modest. For example, PoE is useful for IP telephones, wireless access points, cameras with pan tilt and zoom, and of course remote Ethernet switches. PoE can provide a long cable that runs up to 330 ft and delivers 12W of isolated power.
PoE is not your only option, though, there are similar technologies that would give you the data and power feature. Let's take a look at them, so you can decide which is the best fit for you.
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) provides both data and power, but it is designed for short cables with a maximum length of 16 ft and provides less than 2.5 W of non-isolated power. It's less expensive than PoE, and works well for low power devices, such as a computer mouse, a headset/microphone, or a serial port.
Other devices, like speakers, scanners, and printers, need more power than USB can provide. IEEE 1394 is similar to USB but can provide substantially more power (45 W) at a distance of slightly over 14.5 ft.
If a device already has power available but no data link, then PoE may not be attractive. A wireless data connection such as IEEE 802.11 may be more economical than running a data cable for the device. Alternatively, there are power line communication technologies that can use power cables for transmitting data. Using some power line modems may be more economical than running a cable.
When data rate and power requirements are both low, other approaches may be viable. Mobile phones, for instance, use batteries for power and antennas for communication. Remote weather sensors use very low data rates, so batteries (sometimes supplemented with solar power) and custom wireless data links are used.
So, make sure you invest in a POE switch.
Depending on the application, some of the advantages with PoE over other technologies are:
Inexpensive cabling
Fast data rate
No batteries required
Peer-to-peer network access (once a device is connected to the network, it's accessible to many users)
Do remote sites in your network not have access to existing LAN? Installing the new infrastructure to accurate LAN is usually too time-consuming and too costly.
Just imagine all the hassle of installing an expensive infrastructure that would deliver LAN to your remote site - assuming that you have the budget for that. This solution would require lots of planning, people, and approvals, often dooming them to failure before they even start.
A managed switch with fiber feature allows you to avoid the hefty price tag that comes with installing LAN lines to your remote sites. With this type of managed switch, you can connect your LAN devices to your network via fiber. A fiber switch is a simple solution to fully connecting your entire network.
You need a high-quality managed fiber switch to connect your devices. A cheaply built managed switch won't give you the reliable connection you need to fully connect your entire network. Without a reliable transport for your data, you'll be susceptible to disruptions in service, and even network outages.
How many times have you had a piece of equipment fail and all that was required to fix it was to simply turn the unit off and on again? You probably agree that it's very frustrating to have to jump in your truck and drive hours to a site just to reboot jammed equipment.
So, to avoid spending money on truck rolls, you need a managed switch that allows you to power on/off and reboot all your critical devices right from your desk at your office. You should be able to operate controls, check temperature at the site, and keep tabs on power consumption - all without rolling a single truck.
In a nutshell, these are the benefits of having a managed switch with power capability:
You've learned what makes an efficient managed switch and how you can protect your network with them. Now let's imagine the following situation:
Your remote site begins to overheat. Your remote site begins to overheat. Your switch is at the site, but not even the best cheap managed switches can send you alerts. You have no idea the temperature is steadily rising and it eventually reaches a critical point, causing your valuable equipment to shut down and even fry. You finally realize the damage when your customers start calling and complaining about the disruption to their service.
Imagine if you had known the temperature was rising before it damaged equipment and crippled your network? Having this power could be the difference between one giant headache and preventing a critical outage.
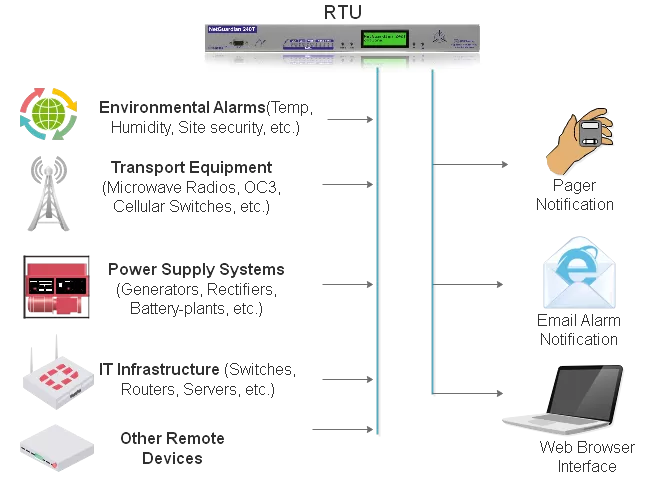
Why stop there? It may seem strange, but did you know that an RTU (Remote Telemetry Unit) will function as a switch, a monitoring device, and a remote control device? With built-in serial server functionality, the right RTU can give you remote access and control to the external devices on your network. Having this remote control can save tons of money and time, and is perfect for managing your remote sites and other distant locations in your network.

RTUs can provide you with additional security for your network. Your valuable equipment is exposed to dangerous environmental conditions every day. Threats like temperature, humidity, and water can cause serious damage to your equipment - which results in giant repair bills, lost revenue, and throngs of angry customers ready to take their business elsewhere.
You don't have to be one of the unprepared ones who suffer from a crippling network outage. This kind of damage is easily prevented, without breaking your budget. You just have to select the right RTU.
So, remember: there's no reason to limit yourself to the functions of a managed switch only. If you want to get the greatest ROI, I recommend looking into an RTU with a built-in switch. With a quality RTU, you'll get not only the remote monitoring and control functionality, but also all the previous that make a managed switch efficient (PoE, fiber switch, and power toggle).
Switch monitoring is very important to keep your network system up and running as it should. However, there is very little useful information available out there about choosing an effective switch monitoring system.

Why is there so little information about switch monitoring when it's vital for network upkeep?
Most companies simply don't have the expertise, and those that do usually aren't client-focused and refuse to share it without massive consultation fees.
That's why our monitoring experts have created the Telecom Switch Monitoring as a practical resource guide. Our intent is to provide you with the essential information you need to choose the best monitoring solution for your network.
The Telecom Switch Monitoring White Paper provides a thorough summary of what you need to know about switch monitoring in a quick and easy-to-read format. It also contains case studies of real-world professionals within the telecom industry. These studies highlight the successful deployments of monitoring systems and the essential role of switch monitoring in real-world networks.
You'll be able to choose the right equipment, protect your revenue, and work on other important job responsibilities. Monitoring isn't your only job, after all.
So, don't wait any longer, click here to download your free copy of the Telecom Switch Monitoring White Paper.

Morgana Siggins
Morgana Siggins is a marketing writer, content creator, and documentation specialist at DPS Telecom. She has created over 200 blog articles and videos sharing her years of experience in the remote monitoring industry.