How Internet of Things (IoT) Monitoring Improves a Network
The Internet of Things (IoT) architecture promises to make our world much more convenient. Ordinary devices are increasingly IP-enabled. Houses, phones, cars, refrigerators, and more are all connected, allowing you to remotely start your car, turn on the lights in your home, and see what's in the fridge while you're shopping.

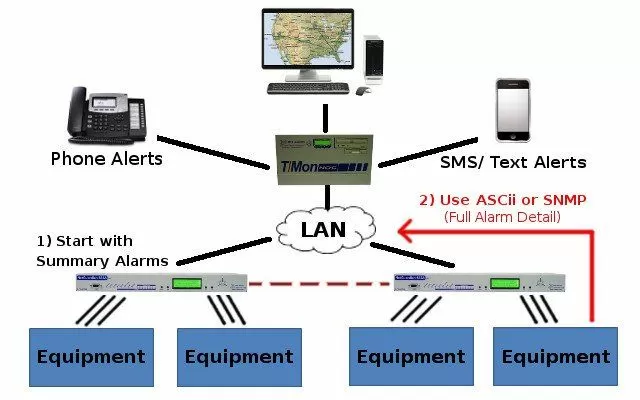
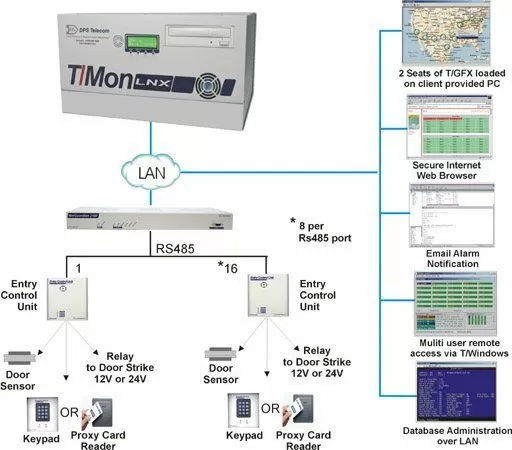
This IoT network diagram is one example of a network of IP enabled devices. These "smart" connected devices are all connected and work together to automate and manage other equipment from a data center.
But the IoT concept reaches beyond just our personal lives and has practical applications in telco-grade networks. Although many elements of IoT devices (constant connectivity, many interconnected devices) have been a core part of remote monitoring in telecom for decades, IoT solutions offers new capabilities to make your job easier.
The transition to IP networks has largely occurred. Remaining legacy connections like serial and POTS modems are increasingly rare. So, what are the next big IoT developments for network monitoring tools?
Next steps for IoT monitoring systems in Telecom:
- Monitoring of more and more devices in the network
Improving technology means that monitoring devices can get smaller and less expensive. Also, many devices will be natively tied to your IoT system. - Artificial Intelligence (AI) for automated insights and reactions to events
With the comprehensive data you're collecting, IoT can apply smart algorithms to improve your system performance. One example that exists today is the HVAC Controller from DPS. This device manages several HVAC devices in lead-lag configurations and makes automatic optimization decisions. - Data trending and optimization
Good central masters in IoT systems can trend data across time. This helps you to detect gradually declining performance that is impossible to see in a snapshot. More advanced systems can even automatically detect these types of problems and bring them to your attention.

The master station helps to give an over all view of the health of the network. Use it to control devices, sensors, and even building access, all while recording data and analytics.
What to look for in a business-grade IoT system:
- Open standards - so all devices can talk to each other. Protocols such as SNMP, DNP3, Modbus, etc. are open standards and are most common so theres little to no need for mediation devices.
- A central master platform - one that can integrate all your devices and help automate processes.
- Using larger devices if needed to reduce complexity when possible rather than more and more separate devices all clustered at the same site.
- Security - it's a major issue for remote sites. SNMPv3, SSH, HTTPS, and RADIUS provide layers of protection in an environment that is prone to hacking.
Ways IoT can improve your monitoring:
- Automation: IP-enabled devices can be pre-programmed for intelligent response to events. Your equipment can email your propane company when your fuel levels are low or your battery backups turned on when theres a commercial power failure.
- Reduce waste: Devices with analytics can help you understand waste in your network (such as inefficiencies in HVAC units).
- Monitor small locations: Smaller devices are less expensive, meaning you can monitor small locations and lesser equipment that would have previously been unmonitored to save cost. More remote monitoring also reduces windshield time!
IoT is a new frontier, but the underlying tech and concepts are not new. Choose a company with a history. Choose someone who can point to a history of success with remote sensing and remote management, etc.