Download our free SNMP White Paper. Featuring SNMP Expert Marshall DenHartog.
This guidebook has been created to give you the information you need to successfully implement SNMP-based alarm monitoring in your network.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayThe basics of SNMP: SNMP Tutorial
SNMP remote monitoring is a vital function for any company with a large network. When you have a network that isn't isolated within a single area, you need assistance to manage it remotely. Integrating monitoring SNMP protocols allows you to streamline remote network visibility. There's just no way (at least, no economical way) to station a live human being at each remote site to monitor everything that happens there.
What distinguishes SNMP remote monitoring from other types of remote monitoring is the use of SNMP ("Simple Network Management Protocol") to transmit messages between central alarm master (an SNMP manager, by definition, in this case) and the SNMP remotes at each network site. This makes monitoring SNMP systems ideal for large-scale, distributed networks. As we discuss more SNMP pros and cons, you'll notice the pros of SNMP are many, and the cons are quite few.
One of the benefits of SNMP - even possibly the main advantage of SNMP - is that it is an open standard. Open protocols are designed to combat the wasted effort and costs when one manufacturer develops its own "proprietary" protocol that only it will support. Utilizing open-standard SNMP monitoring ensures scalability and compatibility with a wide range of devices. Anyone who buys remote monitoring devices that use these protocols is asking for trouble. The manufacturer may raise prices with little threat of damaging sales volume, since they are "the only game in town." Worse yet, the manufacturer may close up shop. At this point, there is no way to get new products or parts to add or repair your remote monitoring system. You'll most likely end up suffering with a dead-end system rather then switching over to a new system all at once. There's no way to gradually transition between systems if one side doesn't work with the other.
The cons of SNMP, which are small compared to its openness, include security risks that are normal whenever using an open standard. There is "security through obscurity" linked with any little-used communications standard. Monitoring SNMP traffic securely - especially using SNMPv3 - is crucial to mitigating these risks. Still, the release of SNMPv3 added new encryption and privacy options that had never before existed within SNMP.
SNMPv3 introduces robust security measures by defining specific security models and levels that enhance data protection:
SNMPv3 also defines three distinct security levels, each providing different degrees of protection:
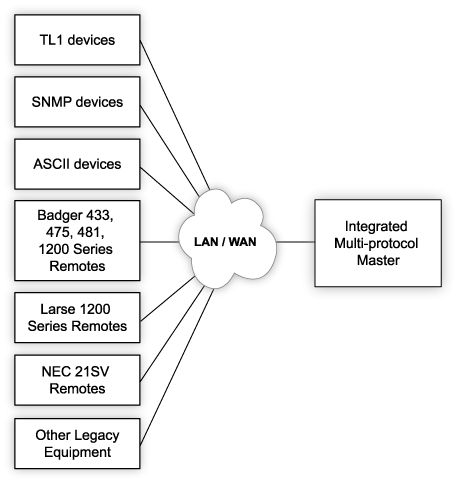
SNMP is also a rather detailed protocol. Detailed messages are sent between devices, not just small preset codes. This downside has been rendered quite small in most applications, since bandwidth has skyrocketed in recent years. In an SNMP remote monitoring system, the two major components are an SNMP manager and SNMP agents.
The SNMP Manager is the central console used by a human operator. It sorts alarm data received from each remote SNMP agent throughout the network. Efficiently monitoring SNMP managers can significantly reduce response times. Additionally, the SNMP manager is responsible for initiating requests to gather data from devices and processing the collected information to generate insightful reports and trigger necessary alerts.
SNMP Agents are located at remote sites, and they fall into two major groups. A lot of modern gear supports SNMP natively. It can send its own alarm messages to the SNMP manager directly. Since not all gear that must be remotely monitored is SNMP-capable, however, SNMP remotes are also required. These devices accept alarms from non-SNMP gear, usually in the form of a discrete contact closure. The alarm remote, which is SNMP-capable, then sends an SNMP message back to the SNMP manager. In this way, both SNMP and non-SNMP devices can be managed under the same SNMP manager group.
How to choose the right SNMP remote
How to choose the right SNMP manager
Beyond these primary components, SNMP monitoring also involves:
Understanding these components and their interactions provides a comprehensive view of how SNMP monitoring operates, ensuring both SNMP-enabled and non-SNMP devices are efficiently monitored within the same network infrastructure.