Download our free SNMP White Paper. Featuring SNMP Expert Marshall DenHartog.
This guidebook has been created to give you the information you need to successfully implement SNMP-based alarm monitoring in your network.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayObject Identifiers (OIDs) are unique numeric or alphanumeric values used to identify objects in databases and networking protocols like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol, where SNMP MIB files contain many OIDs). They act as unique references to data objects, allowing systems to efficiently manage, retrieve, and update data. For organizations such as public safety or indigent defense systems, clear object identification is critical for operational integrity.
Data Type: Object identifiers are typically represented as unsigned four-byte integers. This means they are whole numbers without a sign and have a limited range, which can be a constraint in large-scale databases. Such constraints can be particularly impactful in high-security environments, including defense systems.
Operations: OID data has limited operations available. It is primarily used for comparing OIDs against themselves. However, you can convert these identifiers to standard integers to perform more complex operations using typical integer functions. It's important to watch out for signed vs. Unsigned discrepancies when doing this conversion. This precision is needed when deploying OIDs in systems supporting indigent defense infrastructure. This way, you can ensure data integrity and compliance.
System Table Management: OIDs are central elements for managing system tables which store metadata about database objects. In defense systems, these tables could include sensitive operational data that requires consistent monitoring and updating.
Aliases and Lookup: OIDs can also be assigned aliases. This is often done with a prefix or name. These aliases simplify the lookup process by allowing the use of readable names instead of raw numeric values. The aliases come with input and output routines that facilitate working with these symbolic names easily. This feature enhances system accessibility, even in mission-critical applications like indigent defense.
In summary, these identifiers play an important role in the internal workings of database systems, primarily in system-level object management. By enabling unique identification and easier name-based referencing through aliases, they streamline interaction with the underlying database infrastructure. These efficiencies can make the difference in life-critical defense systems, ensuring rapid response and operational clarity.
If you're a professional responsible for your organization's large-scale network management system, read on. Here we will break down the concept of OIDs so you can take that knowledge with you onto the job and keep your enterprise's operations running smoothly.
SNMP Definition: Simple Network Management Protocol is an application-layer protocol that allows for the exchange of monitoring and managing information between network devices.
Once you can answer "what is OID in networking?" you can explore how to retrieve the numerical OID for a named object in SNMP. To get an SNMP object's OID, you'll typically:
The format of an OID tree can be confusing at first. It's a huge string of numbers like this:

The first part of the OID will be the same for every piece of equipment you'll ever use:
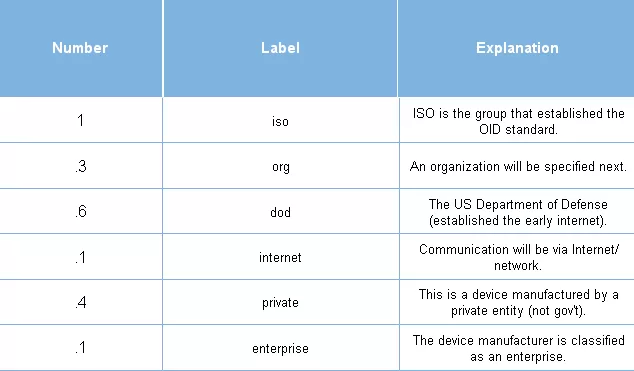
So far, we know that a private enterprise will be declared as the manufacturer of this SNMP device. This will be true for virtually every network device you work with. That makes "1.3.6.1.4.1..." an almost-universal prefix to OIDs. Let's continue:
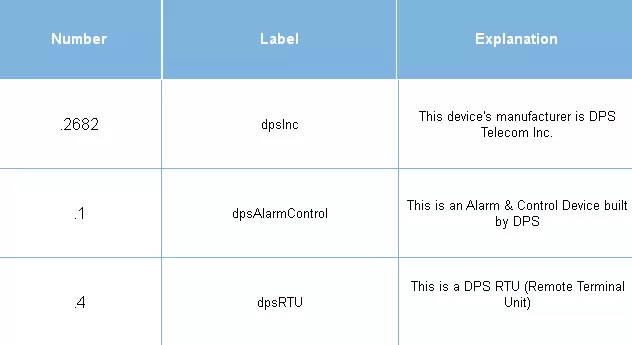
If you have questions about DPS RTUs, you can ask them here. Notice how long the "device manufacturer" number is ("2682"). There are a lot of manufacturers out there, and they all must have a unique integer value. This section of the OID also told us that we're working with an RTU, which collects alarms from non-SNMP equipment.
Native SNMP gear would have a different OID value here. Let's finish reading this OID now:
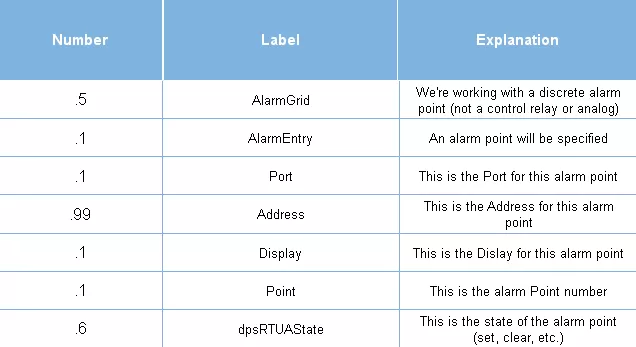
Now you know that you're dealing with the state of discrete alarm point #1 on an RTU manufactured by DPS Telecom. Not bad for a string of numbers, huh?
OIDs are defined in the SNMP MIB file, a kind of "codebook" for SNMP. The manufacturer (DPS Telecom in this example) spells out the second half of the OID for their own devices by supplying a MIB file to their users. The first half is established by a standard referenced "RFC" MIB used worldwide.
Let's Consider the OID From a Slightly Different Angle Now...
To monitor network alarms, you must know your alarm points. Your apartment or house address indicates a specific location by country, state, city, zip code, street, and house number. SNMP systems have OIDs that define each thing for the SNMP agents and manager.
We can compare MIB to OID as being similar to a domain name to an IP address.
OIDs point to network monitoring objects stored in a database called the Management Information Base (MIB). A MIB object holds the structure of the network alarms being monitored (like a map of the "city"), and it uses the OIDs to keep track of the individual components (like the address to a house or other location).
In this example, an SNMP OID is like the address the fire truck would drive to if the fire alarm sounded. What if a fire broke out at your house, and you called the fire department with GPS coordinates (representing the Object ID or OID)? The fire department would have to look that up in its MIB to determine the correct street address.
In telecom, SNMP OIDs describe specific locations in the managed network. This allows the MIB to translate the location of the event into a status description for your network administrators.
1.3.6.1.4.1.2681.1.2.102
Download the Complete SNMP White Paper: It's a quick, 12-page SNMP Introduction by Marshall DenHartog where you'll learn about traps, message formats, the MIB, and other fundamental SNMP concepts.
While it may look daunting, the OID follows a simple structure, with each "dot" segment identifying a part of a network element. Going back to the home address example, the beginning of the Object Identifier tells us the hemisphere of the world, the country, state, city, zip code, street address and eventually leads us to our driveway. In the above OID, the specific "driveway" is 102. With this structure, very specific elements can be identified and located even in very complex networks.
An SNMP Manager (ex. T/Mon LNX) translates these SNMP OIDs into a value that is then assigned readable labels in the MIB. This allows the SNMP manager to produce messages that can be read by people.
When the SNMP Manager, a T/Mon, in this case, will collect information by requesting the value ("state") of any object it is monitoring, it sends a message with that object's OID to its Management Information Base. The MIB will decode the address and attach a text description to it. This allows the SNMP Manager to present the value of the alarm condition with the identifying description of the labeled alarm.
So for example, let's say the SNMP Manager wants to know if there is a car in the driveway of your house (a "yes or no" question, often referred to as a discrete alarm in the alarm monitoring world). The SNMP Manager would look up the corresponding reference in the MIB in order to "poll" (ask) if there is a car in the driveway at 123 Main St. The MIB references 123 Main St. and translates it into the OID of your driveway.
In our example OID above, it would be 123 Main St = 1.3.6.1.4.1.2681.1.2.102. The driveway (or alarm point we want to monitor) would be represented by the "102" portion of the address. The "value" reported is the current state of the driveway 102 : occupied by a car or not.
The sensor at the driveway reports back: Nope. Nobody's in the driveway.
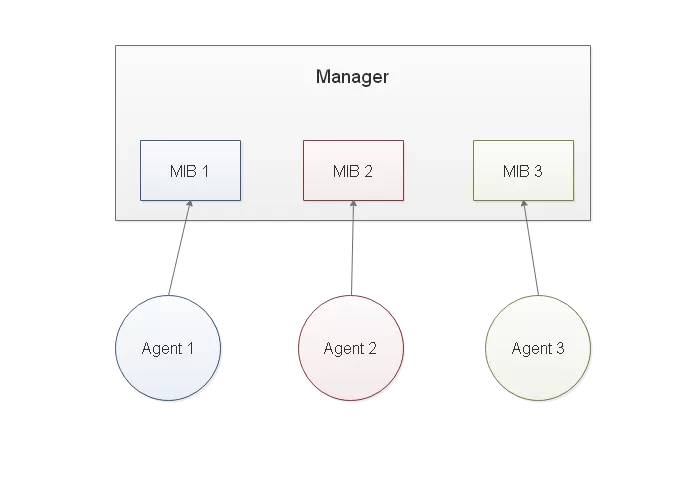
This message is captured by the SNMP Manager which again uses the Management Information Base to tie the OID sensor message that was reported by the "driveway sensor" (a simple "No" response) back into the human-readable 123 Main St. which is displayed.
If an SNMP managed object does not have an OID listed within a MIB, the SNMP Manager cannot identify it. Even if that object has a sensor and can transmit data, the SNMP Manager is blind without the MIB. For a condition or device to be monitored, it must have a corresponding MIB definition.
To find SNMP OIDs using a MIB browser, you'll typically follow a straightforward process. First, load the appropriate MIB file(s) related to your device or application into the MIB browser. These MIB files contain definitions for the OIDs and help translate the numeric OIDs into more understandable labels. Once the MIBs are loaded, you can browse through the hierarchical tree structure presented by the browser to locate the OID you need. This tree is organized logically according to the structure defined in the MIBs. This makes it easier to find specific OIDs based on their function or device category.
If you're looking for a specific SNMP OID, you can use the search functionality within the MIB browser. Enter a keyword related to the OID (such as part of the OID name or description) into the search bar. The browser will then filter through the loaded MIBs to find matching OIDs. This method is especially useful when dealing with large MIB files or when you're unsure of the exact OID you're looking for.
Other tools that can help you find a device's OID and related MIBs include iReasoning MIB Browser, ManageEngine MibBrowser, and SolarWinds Engineer's Toolset. These tools are designed to make the process of navigating MIB files, finding OIDs, and testing SNMP queries straightforward and efficient.
Finally, remember that the first several pieces of each OID are almost always the same. These upper location levels are defined by a series of standard reference within the MIB. These series are called RFCs, or Requests for Comments.
The RFCs that define SNMP OIDs are part of a larger group of RFC documents that define the Internet as a whole. Individual vendors create their own SNMP enterprise MIBs that only include the OIDs for their devices.
If you have unique requirements, look for a vendor that can create custom SNMP MIB files.
Here at DPS, we will occasionally have clients that require specific MIBs for their applications. One client, James, needed to be able to identify all of the printers on his LAN via SNMP by asking every device for its OID at user-defined time intervals. He needed to email any reporting events to the SNMP monitor, and he had to do that without busting his budget.
Another client had a need to send certain SET commands to remote units at some microwave sites. The units were not capable of sending those commands. Our solution had custom OIDs that were configured with variable bindings to accept SNMP Traps. This allowed monitoring and control of the remote microwave sites with the ability to toggle up to 40 discrete relays in the managed system.
This solution saved them money and downtime and increased the use of existing equipment for the customer.
At DPS, we've worked on thousands of projects that involve SNMP in one form or another. With Veteran SNMP experts on staff ask us a few questions by sending us a quick online message (or call 1-800-693-0351)
Related Articles
All DPS Telecom products include comprehensive technical support. If you've purchased one of our products and are encountering any kind of issue, contact DPS Tech Support today at 559-454-1600.
At DPS Telecom, the representative who answers your call isn't an intern reading from a script. DPS Tech Support representatives are engineers who contribute to product development. And, if your problem requires additional expertise, the DPS Engineering Department that designed your product is right down the hall.
Help us connect you to the right engineer by filling out this quick questionnaire. Simply leave your contact information to get started, and we'll call you back. Most preliminary discussions are about 15 minutes, and afterward, we'll send you a custom application diagram of a recommended solution that'll make it easier to justify your project to management.